Outsiders equity or external equity refers to the funds that a company raises from individuals or organizations that are not a part of the company's ownership structure. Outsiders equity can come in many forms, such as equity financing, bond financing, and other forms of long-term borrowing. It is an essential part of a company's capital structure, as it provides the necessary funds for a company to grow and expand. Before delving into outsiders equity, it is essential to understand the concept of equity itself. Equity refers to the ownership interest in a company. When you own equity in a company, you are a shareholder, and you own a piece of the company. The value of your equity stake in the company is directly tied to the company's performance. There are two primary types of equity: common equity and preferred equity. It is the most basic form of equity, and it represents ownership in the company's common stock. Common equity holders have the right to vote on matters such as electing the board of directors and making changes to the company's bylaws. They also have the right to receive dividends, although these dividends are not guaranteed. It is a type of equity that gives its holders priority over common equity holders when it comes to receiving dividends or distributions. Preferred equity holders also have priority over common equity holders in the event of a company liquidation or bankruptcy. Equity is an essential component of a company's capital structure. Without equity, a company would have to rely solely on debt financing, which can be risky and expensive. Equity provides a cushion of protection for a company's lenders, as equity holders are the last in line to receive payments in the event of bankruptcy or liquidation. Equity also gives a company the flexibility to pursue growth opportunities. Unlike debt, equity does not have to be repaid on a set schedule, which allows a company to invest in its future without being bogged down by debt payments. Equity and debt financing are two primary ways that companies can raise capital. While both involve raising money from outside sources, there are significant differences between the two. This involves borrowing money that must be repaid on a set schedule, usually with interest. The lender does not become an owner of the company, but rather is entitled to receive payments according to the terms of the loan agreement. This involves selling ownership stakes in the company to outside investors. These investors become owners of the company and are entitled to a share of its profits. Unlike debt, equity does not have to be repaid on a set schedule. Internal equity refers to the funds that a company raises from its existing shareholders. This can be done through the issuance of new shares or through the reinvestment of profits back into the company. External equity, as we have discussed, refers to the funds that a company raises from individuals or organizations that are not a part of the company's ownership structure. Internal equity and external equity differ in several ways. Internal equity is typically less expensive than external equity, as there are no transaction costs associated with issuing new shares. Internal equity also does not dilute the ownership stakes of existing shareholders, as new shares are issued only to them. External equity can be more expensive than internal equity, as there are transaction costs associated with issuing new shares or borrowing funds. External equity can also dilute the ownership stakes of existing shareholders, as new shares are issued to outside investors. One benefit of internal equity is that it allows a company to retain control over its ownership structure. By issuing new shares only to existing shareholders, a company can ensure that its ownership remains concentrated among a small group of investors. Internal equity also allows a company to avoid the costs and regulatory requirements associated with issuing new shares to outside investors. However, internal equity also has some drawbacks. By only raising funds from existing shareholders, a company may limit its ability to grow and expand. Existing shareholders may not have the financial resources to provide all the capital that a company needs, and they may also be hesitant to invest additional funds in a company that is not performing well. External equity, as we have discussed, can provide a company with the funds it needs to grow and expand. By bringing in new investors, a company can tap into a wider pool of capital and potentially access funding sources that may not be available through internal equity. However, external equity also has some drawbacks. External equity holders may have different goals and objectives than existing shareholders, which can lead to conflicts and disagreements. Outsiders equity refers to the funds that a company raises from individuals or organizations that are not a part of the company's ownership structure. This can include equity financing, bond financing, and other forms of long-term borrowing. Some examples of outsiders equity include: Common Stock: Companies can issue new shares of common stock to outside investors in exchange for funds. Preferred Stock: Similar to common stock, preferred stock gives its holders priority over common equity holders when it comes to receiving dividends or distributions. Convertible Bonds: These are bonds that can be converted into equity at a later date. Warrants: These are securities that give their holders the right to purchase shares of common stock at a set price. Outsiders equity has several key features that differentiate it from other forms of financing: Long-Term: Outsiders equity is typically a long-term source of financing, as investors expect to receive a return on their investment over a period of several years. No Set Repayment Schedule: Unlike debt financing, outsiders equity does not have to be repaid on a set schedule. Ownership Stake: Outsiders equity investors become owners of the company, which means that they are entitled to a share of the company's profits and have a say in the company's operations. Variable Returns: The returns on outsiders equity investments can vary widely depending on the company's performance. Outsiders equity is an essential source of financing for many companies, particularly those that are looking to grow and expand. By bringing in outside investors, a company can access a wider pool of capital and potentially tap into funding sources that may not be available through internal equity. Outsiders equity also allows a company to spread its risk among a larger group of investors. Rather than relying on a small group of internal equity holders, a company can bring in outside investors who are willing to share in the risk of the company's operations. There are several common sources of outsiders equity that companies can tap into: Initial Public Offerings (IPOs): An IPO is when a company goes public and offers shares of its stock to the general public for the first time. Private Placements: Private placements involve selling shares of stock to a select group of investors, such as institutional investors or high net worth individuals. Venture Capital: Venture capital firms invest in early-stage companies that have high growth potential. Angel Investors: Angel investors are typically wealthy individuals who invest in early-stage companies. Each source of outsiders equity has its advantages and disadvantages. IPOs, for example, can be a highly visible way for a company to raise capital and can generate a significant amount of funding. However, going public also comes with significant regulatory and reporting requirements, and the costs associated with an IPO can be high. Private placements, on the other hand, can be a more cost-effective way for a company to raise capital. However, the pool of potential investors is smaller, and companies may have to comply with securities laws and regulations. Venture capital and angel investors can provide early-stage companies with the funding they need to grow and expand. However, these investors may demand a significant ownership stake in the company, and the terms of the investment may be restrictive. Before choosing a source of outsiders equity, companies should consider several factors, including: Amount of Funding Needed: Different sources of outsiders equity may be more appropriate for companies that need different levels of funding. Growth Potential: Some investors may be more interested in companies that have high growth potential. Industry: Different sources of outsiders equity may be more appropriate for companies in different industries. Regulatory Requirements: Some sources of outsiders equity may come with more regulatory and reporting requirements than others. The steps to raise outsiders equity can vary depending on the source of funding. However, some common steps include: Identifying Potential Investors: Companies should identify potential investors that may be interested in investing in the company. Preparing a Pitch: Companies should prepare a pitch that explains their business model, growth potential, and how the funds will be used. Negotiating Terms: Companies should negotiate the terms of the investment with potential investors. There are a handful of factors that can affect outsiders equity, including: The overall state of the economy can have a significant impact on outsiders' equity. In a strong economy, investors may be more willing to invest in companies, as they believe that the companies will perform well. In a weak economy, however, investors may be more hesitant to invest, as they are concerned about the company's ability to generate returns. The conditions of the industry in which a company operates can also impact outsiders' equity. Investors may be more interested in companies that operate in industries that are growing and have high potential for future growth. On the other hand, companies in declining industries may find it more challenging to raise outsiders' equity. The financial status of a company can also impact its ability to raise outsiders' equity. Companies that have a strong financial position, with high revenue and profits, are more likely to attract investors than companies that are struggling financially. Investors are often looking for companies that have high growth potential. Companies that have a clear path to growth, such as through expanding into new markets or launching new products, are more likely to attract investors than companies that do not have a clear growth strategy. Investors may also consider a company's creditworthiness when deciding whether to invest. Companies with high credit ratings are more likely to attract investors, as they are seen as less risky investments. Outsiders equity, in the form of publicly traded stocks, is bought and sold on the stock market. When a company goes public, it issues shares of its stock to the general public. These shares are then traded on stock exchanges such as the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) or the NASDAQ. Investors can buy and sell shares of publicly traded stocks on these exchanges through a broker. When an investor buys a share of stock, they become a part owner of the company and are entitled to a share of the company's profits. When they sell a share of stock, they receive the market price of the share at the time of the sale. Outsiders equity is an essential source of financing for many companies. By bringing in outside investors, companies can access a wider pool of capital and potentially tap into funding sources that may not be available through internal equity. However, outsiders' equity also comes with some risks. By bringing in outside investors, companies dilute the ownership stakes of existing shareholders and potentially lose control over their operations. Companies must carefully consider the advantages and disadvantages of each source of outsiders equity before deciding which one to pursue. Overall, outsiders' equity plays a critical role in the global economy. By providing companies with the funds they need to grow and expand, it helps to drive innovation and create new jobs. Investors play a critical role in this process, providing the capital that companies need to succeed.What Is Outsiders Equity?
Understanding Equity
Types of Equity
Common Equity
Preferred Equity
Importance of Equity
Difference Between Equity and Debt Financing
Debt Financing
Equity Financing
Internal Equity vs External Equity
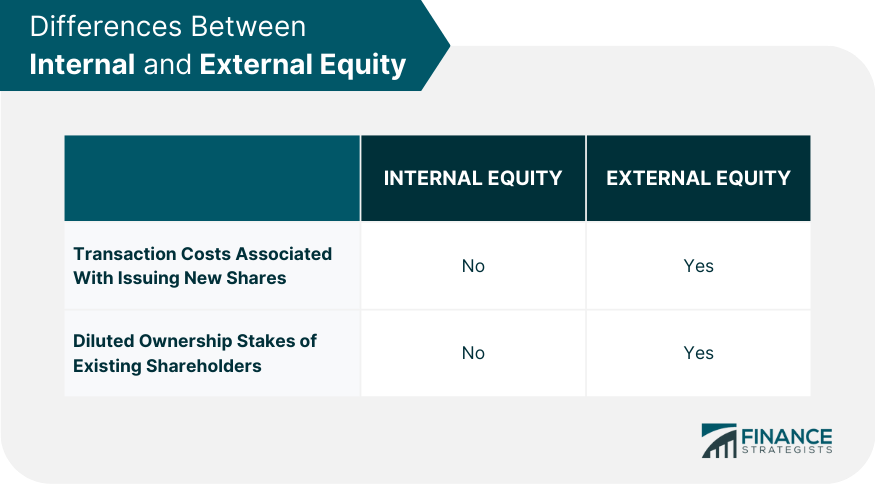
Benefits and Drawbacks of Internal Equity
Benefits and Drawbacks of External Equity
Definition of Outsiders Equity
Examples of Outsiders Equity
Features of Outsiders Equity
Importance of Outsiders Equity to Companies
Common Sources of Outsiders Equity
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Source
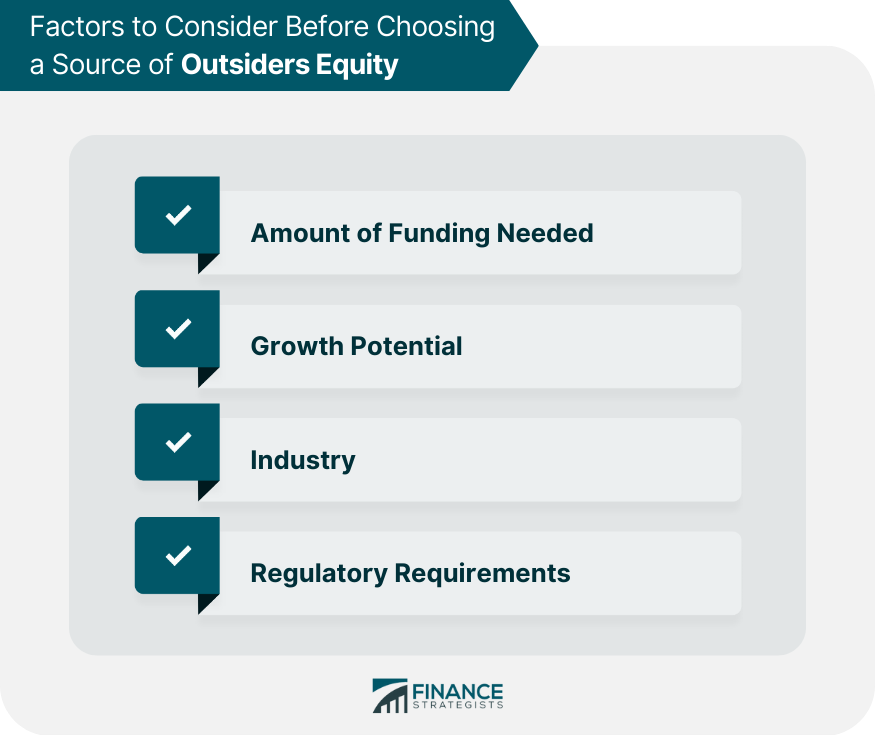
Factors to Consider Before Choosing a Source of Outsiders Equity
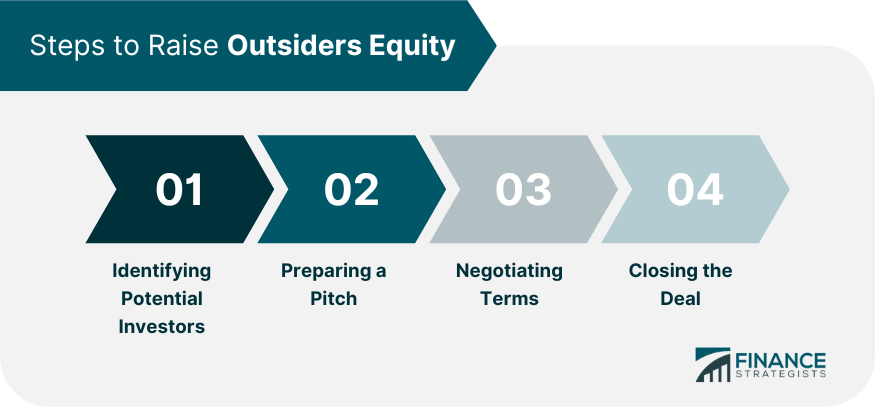
Steps to Raise Outsiders Equity
Factors Affecting Outsiders Equity
Economic Conditions
Industry Conditions
Company's Financial Status
Company's Growth Potential
Company's Creditworthiness
How Outsiders Equity Is Traded in the Stock Market
Conclusion
Outsiders Equity FAQs
Internal equity refers to the funds a company raises from its existing shareholders, while external equity refers to the funds a company raises from individuals or organizations that are not part of the company's ownership structure.
Common sources of outsiders equity include initial public offerings (IPOs), private placements, venture capital, and angel investors.
Outsiders equity allows a company to access a wider pool of capital, spread its risk among a larger group of investors, and pursue growth opportunities without being bogged down by debt payments.
Outsiders equity can dilute the ownership stakes of existing shareholders and potentially lead to a loss of control over the company's operations. External equity holders may also have different goals and objectives than existing shareholders, which can lead to conflicts and disagreements.
Outsiders equity, in the form of publicly traded stocks, is bought and sold on stock exchanges such as the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) or the NASDAQ. Investors can buy and sell shares of publicly traded stocks on these exchanges through a broker.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















